 |
Analysis Internet Development in China: An Analysis of the CNNIC Survey Report By Peter Weigang Lu II. IS THE NUMBER OF CHINA INTERNET USERS REPORTED BY CNNIC CREDIBLE? Number of Computers connected to the Internet: 3.5 million Number of Internet Users: 8.90 million (Excerpt from CNNIC Jan. 2000 Survey Report)
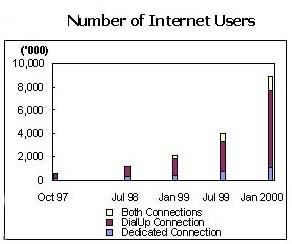 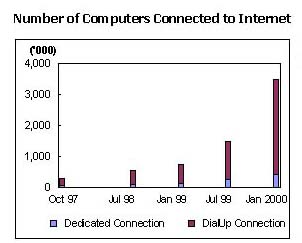 It seems that quite a lot of people would rather not believe the number of China Internet users CNNIC reported for the year 1999. After all, the CNNIC report claimed more users than any of the above-mentioned reputed research houses had predicted. There are no generally accepted definitions for an Internet user. Statistical reports from many countries define an Internet user as a person who has accessed the Internet in the 12 months preceeding the gathering of data for the report. Research houses define an Internet user as a person going online at least once in a recent period, ranging from four weeks to three months. A person who accesses the Internet on a weekly or monthly basis is regarded as a frequent or regular Internet user. The CNNIC report offered no definition of Internet users. The most recent report, released Jan. 2000, said the average time China's Internet user spent online was 17 hours per week, but it did not give out the distribution of time spent among the users as the previous reports did. The table below is the distribution revealed in CNNIC's July 1999 survey report. 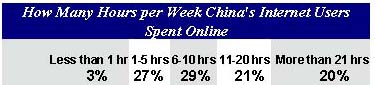 If this distribution held true for respondents to CNNIC's January 2000 survey, 97 percent of China's total Internet users in 1999 could be, in fact, frequent or regular users. Any online survey that solicits respondents rather than randomly samples the population has the inherent fault of skewed distribution. The large number of entries in CNNIC's January 2000 survey can only moderate the skewing effect. In this regard, we may reckon that users accessing the Internet less frequently and spending less time online are less likely to have a chance to see the survey hyperlinks and hence less willing to take at least 20 minutes to fill in the CNNIC survey questionnaires. Even taking that into consideration, however, it is safe to say the great majority of China Internet users are frequent, even regular, users. To test the credibility of the CNNIC number, the ratios between computers with Internet access and Internet users over the 1997-1999 period are calculated and shown in the table below. The percentage of dial-up computers among total Internet-accessible computers, as well as the percentage of dial-up service users among total Internet users rose substantially from the end of 1998, while the average number of persons sharing a common account to access the Internet dropped. We do not see any possibility for a bloated number of Internet users. Additionally, the fact that dial-up computers accounted for nearly 90 percent of the total Internet-accessible computers in 1999 also indicates there is little room to manipulate the number of Internet accessible computers. CNNIC, in its unique position, has easy access to the statistics of the number of dial-up access subscribers nationwide.
Note: Users with both connections have been taken into account in calculating ratios for Dedicated and Dial-up Connections. It is worth noting that more than 2 persons sharing a dial-up account in China is very normal, as a great proportion of dial-up subscribers are actually small and medium-sized businesses. In all, we firmly believe that by the end of 1999, China had an Internet population of 8.9 million, of which the majority of users were frequent users by any definition. |
 This Article Previous Articles
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Infotech: News | Analysis | Reviews | Perspectives | Events | Resources Home | Search | News | Trade | Finance | Infotech | Leisure | Shop |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ©1999 - 2000 Virtual China, Inc. All rights reserved. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||